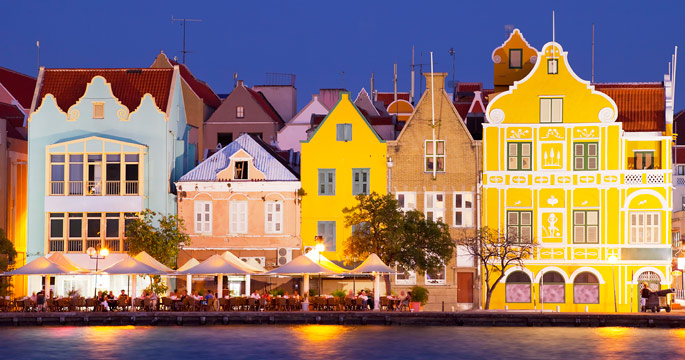There’s more to the Caribbean than beach chairs and boat drinks. The region is rich in history, with cities dating back 500 years to the first days of European influence and settlement. Several of the most significant and best preserved of these old towns have earned World Heritage status from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). These five in particular are worth a walking tour, so leave the flip-flops at the resort, and put on your walking shoes to discover the Caribbean’s deeper roots.
Historic Bridgetown, Barbados
Barbados was one of England’s first settlements in the Caribbean. Blessed with a protected natural harbor, the port of Bridgetown grew to become the British Empire’s most important military and commercial center in the region. Unlike Dutch and Spanish cities of the time, the streets of Bridgetown were not laid out on an organized geometric grid, and instead copied the serpentine meanderings of medieval-era cities such as London. Today, the city’s well preserved historic district contains a wealth of architectural styles from the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, including a number of the finest examples of British Colonial buildings in the Western Hemisphere. Other highlights include homes built in the Creole-inspired Caribbean Georgian style, and Neo-Gothic Parliament Buildings from the Victorian Era. History buffs may want to visit the George Washington House, where the United State’s first president spent time in the 1750s. A highpoint of any historic tour is the St. Anne’s Garrison. This expansive and well- preserved fortification was home to the British West Indies Regiment throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, and is the surviving southern terminus of a series of fortifications that once ringed the city’s coast along the Bay Street corridor.

Once a lively commercial waterfront lined with warehouses, Bridgetown’s Careenage is now fronted by shops and restaurants, and its pathways are a favorite for afternoon strolls. Photo: iStock
Old Havana, Cuba
Modern Havana is a sprawling city of two million, but tucked into this metropolis is a district of narrow streets and urban plazas, overlooked by buildings exhibiting an eclectic mix of Cuban Baroque, Neoclassical and Moorish influences, and private homes featuring arcades, balconies, wrought-iron gates and internal courtyards. UNESCO considers this area to be “the most impressive historical city centre in the Caribbean and one of the most notable in the American continent as a whole.” As the most important port in the Caribbean, Havana was well guarded by an extensive network of forts, including the Fortaleza de San Carlos de la Cabaña, which is one of the largest colonial fortresses ever constructed in the Americas, and the Castillo de la Real Fuerza, which is one of the continent’s oldest. The city’s surviving ring of protection includes more than a half-dozen additional fortifications, including the iconic Castillo de los Tres Reyes del Morro, which remains one of Cuba’s most recognized landmarks. Mixed in with 16th and 17th century edifices are grand buildings from the days of Cuba’s sugar boom. Most notable among these is the Capitolio Nacional, which was built from white Capellanía limestone and granite to mimic the U.S. Capitol Building.

El Capitolio remained the seat of government in Cuba until the revolution of 1959. Now restored, this historic structure is the home of Cuba’s National Assembly. Photo Michal Krakowiak/iStock
Colonial City of Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic
Founded just six year’s after Christopher Columbus landed on the shores of Hispaniola, Santo Domingo soon became Spain’s most important settlement in the Caribbean. The expeditions of conquistadors such as Ponce de Leon, Cortes and Balboa were launched from this walled city, and by the early 1500s; city founders had established the first cathedral, monastery, hospital, customs house and university in the Americas. From its inception the town was laid out on an orderly grid pattern that would become a model for city planning across the New World. Branching out from the Plaza Mayor, and surrounded by stone and earthen walls, 32 streets and 116 blocks of the original colonial city remain almost totally intact. Any tour of this area should include a viewing of the medieval and Renaissance artworks at the Alcázar de Colón, a tour of Las Casas Reales and a stroll down the Calle de la Damas, which is said to be the oldest street in the Americas.

The Catedral Primada de America is the oldest Catholic Church in the Western Hemisphere. Its first stone was set in 1514 by Diego Columbus, son of the famous explorer. Photo: Adam Berent/Curacao Tourist Board
Willemstad Inner City and Harbor, Curacao
Home to one of the finest natural harbors in the southern Caribbean, the island of Curacao was a natural choice for Dutch traders looking to establish a foothold in the region. Fort Amsterdam was constructed in 1634 to protect the entrance to Sint Anna Bay, and the walled town of Willemstad was added several decades later. Within the ramparts of this fortified outpost, settlers built two- to three-story homes and shops along narrow lots facing even narrower streets. This development mirrored the architectural styles of Dutch cities where urban space was at a premium. This pattern changed in the early 1800s when the encircling fortifications were removed, and the city spread outward to the western side of the bay. Free of walled confines and small lot sizes, builders created more expansive plantation-style houses surrounded by galleries. Today, Willemstad includes four historic districts. The original walled city is known as the Punda district. To the west are the 19th century neighborhoods of Otrobanda, Pietermaai. Scharloo, which showcase a diverse range of architectural styles with Spanish, Iberian and Afro-American influences. One of the historic city’s most distinctive features is the bright red, blue, yellow and green shades of the buildings. This colorful display wasn’t created for aesthetic enhancement, but at the decree of 19th century Governor General Albert Kikkert, who apparently suffered headaches from the glare of whitewashed facades.

Floating on moveable pontoons, the Queen Emma Bridge spans the entrance to Curacao’s St. Anna Bay, connecting Willemstad’s Punda and Otrobanda quarters. Photo: iStock
St. George’s, Bermuda
For nearly 400 years, the islands of Bermuda remained the principal base of the British Royal Navy in the Western Atlantic. Evidence of this military presence can be seen all around the harbor town of St. George’s. Numerous historic stone fortresses and batteries line the entrance to the harbor and perch on small nearby islands. The town itself dates back to 1612, and is recognized as the oldest continuously occupied English settlement in the Americas. Buildings originally built of local cedar wood and palm-thatch roofing did not fare well in passing hurricanes. The enduring legacy of this period is the narrow alleys and lanes of the old town. By the 17th century islanders solidified the distinctive style of architecture that remains a signature of Bermuda to this day, utilizing limestone blocks for walls, and ceramic tile roofs to capture rainwater. The numerous military constructs surrounding the town are of particular interest to military historians, as they include some of the only surviving examples of 17th century defensive works built by early European colonists. Other fortifications of varying ages follow an evolved pattern of design based on the ongoing advances in artillery.

Located in downtown St. George’s, St. Peter’s is the oldest Anglican Church outside the British Isles, and the oldest Protestant church in continuous use in the New World. Photo: iStock